The median income for families is that amount above which half the families have more and below which half the families have less income. It is “in the middle.”
According to the U.S. Census:
Family. A family is a group of two people or more (one of whom is the householder) related by birth, marriage, or adoption and residing together; all such people (including related subfamily members) are considered as members of one family.
Household. A household consists of all the people who occupy a housing unit. A house, an apartment or other group of rooms, or a single room, is regarded as a housing unit. See median household income.
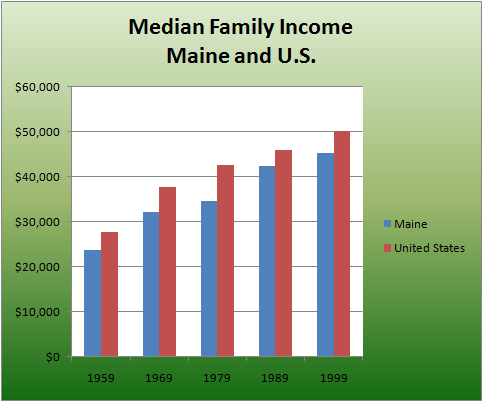
During the five decades 1959 – 1999, median income for Maine families was consistently lower than for the Unites States as a whole. The average difference has been $5,160 or 13% lower than the U.S., but the 1979 difference was much more than the remaining four decades. Taking 1979 out of the calculations, the average drops to $4,444 or 11.5%. In any event, Maine income lags the average for rest of the country. More Economic Data
| Median Family Income | Difference $ | Difference % | ||
| YEAR | Maine | U.S. | U.S.-Maine | U.S.-Maine |
| 1959 | $23,790 | $27,632 | $3,842 | 13.9% |
| 1969 | $32,148 | $37,559 | $5,411 | 14.4% |
| 1979 | $34,587 | $42,609 | $8,022 | 18.8% |
| 1989 | $42,299 | $45,956 | $3,657 | 8.0% |
| 1999 | $45,179 | $50,046 | $4,867 | 9.7% |
| Average: | $5,160 | 13.0% | ||
Source: 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, and 2000 Censuses of Population.
Income Surveys Branch/HHES DivisionU.S.
Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/income/data/historical/state/state2.html
(accessed August 20,2011)